What is an aphorism? How about a heuristic? Sick of platitudes? What in the world is a deepity?
After seeing some of these words over and over again on Twitter—and getting tired of repeatedly searching definitions of them—I decided to make this handy cheat sheet.
Bookmark it for quick reference.
Contents: Click a link here to jump to a section below
- Abstraction
- Adage
- Analogy
- Anecdote
- Aphorism
- Axiom
- Deepity
- Epigram
- Heuristic
- Idiom
- Maxim
- Metaphor
- Parable
- Platitude
- Proverb

The Communication Cheat Sheet — What is an Aphorism, Heuristic, Platitude, Deepity, & More (+ Infographic)
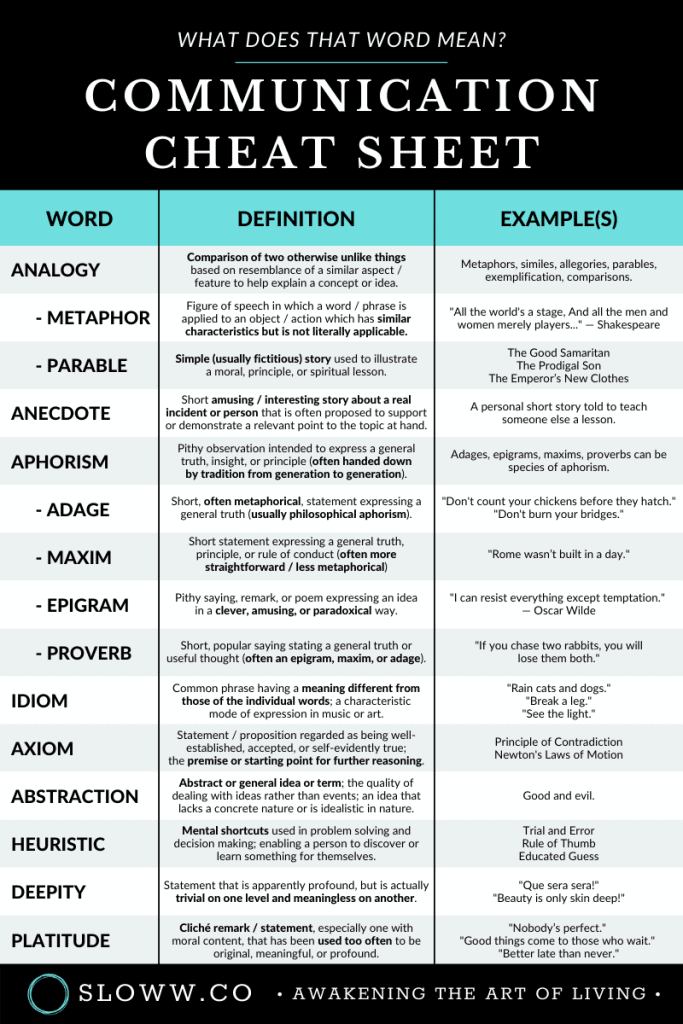
Abstraction
Abstraction Definition: An abstract or general idea or term; the quality of dealing with ideas rather than events; an idea that lacks a concrete nature or is idealistic in nature; the act of considering something as a general quality or characteristic, apart from concrete realities, specific objects, or actual instances.
Abstraction Example: Good and evil.
From Wikipedia (Abstraction):
- Abstraction in its main sense is a conceptual process where general rules and concepts are derived from the usage and classification of specific examples, literal (“real” or “concrete”) signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
- An abstraction is the outcome of this process—a concept that acts as a common noun for all subordinate concepts, and connects any related concepts as a group, field, or category.
- Conceptual abstractions may be formed by filtering the information content of a concept or an observable phenomenon, selecting only the aspects which are relevant for a particular subjectively valued purpose.
Adage
Adage Definition: A short statement expressing a general truth; often in metaphorical form that typically embodies a common observation; usually philosophical aphorism.
Adage Example: “Do not count your chickens before they hatch.” “Do not burn your bridges.”
From Wikipedia (Adage):
- An adage is a concise, memorable, and usually philosophical aphorism that communicates an important truth derived from experience, custom, or both, and that many people consider true and credible because of its long-lived tradition (being handed down generation to generation).
- Adages may be interesting observations, ethical rules, or skeptical comments on life in general.
Analogy
Analogy Definition: A comparison of two otherwise unlike things based on resemblance of a similar aspect / feature (often to help explain a concept or idea).
Analogy Example: Specific analogical language comprises exemplification, comparisons, metaphors, similes, allegories, and parables (e.g. the parables of Jesus are analogies).
From Wikipedia (Analogy):
- A cognitive process of transferring information or meaning from a particular subject (the analog, or source) to another (the target).
- Analogy plays a significant role in problem solving, as well as decision making, argumentation, perception, generalization, memory, creativity, invention, prediction, emotion, explanation, conceptualization and communication.
- It has been argued that analogy is “the core of cognition.”
Anecdote
Anecdote Definition: A short amusing or interesting story about a real incident or person that is often proposed to support or demonstrate a relevant point to the topic at hand.
Anecdote Example: A personal short story told to teach someone else a lesson.
From Wikipedia (Anecdote):
- An anecdote is a brief, revealing account of an individual person or an incident: “a story with a point,” such as to communicate an abstract idea about a person, place, or thing through the concrete details of a short narrative or to characterize by delineating a specific quirk or trait.
- Reveal a truth more general than the brief tale itself.
Aphorism
Aphorism Definition: A pithy observation intended to express a general truth, insight, or principle; typically not as straightforward as a maxim.
Aphorism Example: The concept is distinct from those of an adage, epigram, maxim, principle, proverb, and saying; some of these concepts are species of aphorism.
“Actions speak louder than words.” “You cannot step into the same river twice.”
From Wikipedia (Aphorism):
- An aphorism is a concise or memorable expression of a general truth or principle.
- They are often handed down by tradition from generation to generation.
Axiom
Axiom Definition: A statement or proposition which is regarded as being well-established, accepted, or self-evidently true; used as the premise or starting point for further reasoning or arguments.
Axiom Example: Principle of Contradiction; Newton’s Laws of Motion.
From Wikipedia (Axiom):
- An axiom or postulate is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments.
- In classic philosophy, an axiom is a statement that is so evident or well-established, that it is accepted without controversy or question.
- In modern logic, an axiom is a premise or starting point for reasoning.
Deepity
Deepity Definition: A statement that is apparently profound, but is actually trivial on one level and meaningless on another.
Deepity Example: “Que sera sera!”; “Beauty is only skin deep!”; “The power of intention can transform your life.”
From Wikipedia:
- Generally, a deepity has two (or more) meanings: 1) one that is true but trivial, and 2) another that sounds profound and would be important if true, but is actually false or meaningless.
- Daniel Dennett adopted and somewhat redefined the term “deepity“, originally coined by Miriam Weizenbaum.
Epigram
Epigram Definition: A pithy saying, remark, or poem expressing an idea in a clever, amusing, or paradoxical way; usually in verse form (unlike aphorisms).
Epigram Example: “I can resist everything except temptation.” — Oscar Wilde
From Wikipedia (Epigram):
- A brief, interesting, memorable, and sometimes surprising or satirical statement.
- The presence of wit or sarcasm tends to distinguish non-poetic epigrams from aphorisms and adages, which tend to lack those qualities.
Heuristic
Heuristic Definition: Mental shortcuts used in problem solving and decision making; enabling a person to discover or learn something for themselves.
Heuristic Example: Trial and Error; Rule of Thumb; Educated Guess.
From Wikipedia (Heuristic):
- Any approach to problem solving or self-discovery that employs a practical method that is not guaranteed to be optimal, perfect or rational, but which is nevertheless sufficient for reaching an immediate, short-term goal.
- Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution.
- Heuristics are the strategies derived from previous experiences with similar problems.
- A person develops a heuristic by using intelligence, experience, and common sense.
Idiom
Idiom Definition: A common phrase having a meaning different from those of the individual words; a characteristic mode of expression in music or art.
Idiom Example: “Rain cats and dogs.” “Break a leg.” “See the light.”
From Wikipedia (Idiom):
- An idiom is a phrase or expression that typically presents a figurative, non-literal meaning attached to the phrase; but some phrases become figurative idioms while retaining the literal meaning of the phrase.
Maxim
Maxim Definition: A short statement expressing a general truth, fundamental principle, or rule of conduct; often more straightforward than an aphorism; a simple and memorable rule or guide for living.
Maxim Example: “Rome wasn’t built in a day.”
From Wikipedia (Maxim):
- A maxim is a concise expression of a fundamental moral rule or principle, whether considered as objective or subjective contingent on one’s philosophy.
Metaphor
Metaphor Definition: A figure of speech in which a word / phrase is applied to an object / action which has similar characteristics but is not literally applicable; representative or symbolic of something else; tool used to draw an analogy.
Metaphor Example: “All the world’s a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances…” — William Shakespeare
From Wikipedia (Metaphor):
- A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another.
- It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two ideas.
Parable
Parable Definition: A simple (usually fictitious) story used to illustrate a moral, principle, or spiritual lesson.
Parable Example: The Good Samaritan; The Prodigal Son; The Emperor’s New Clothes.
From Wikipedia (Parable):
- A parable is a succinct, didactic story, in prose or verse, that illustrates one or more instructive lessons or principles. It differs from a fable in that fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as characters, whereas parables have human characters.
Platitude
Platitude Definition: A cliché remark or statement, especially one with moral content, that has been used too often to be original, meaningful, or profound.
Platitude Example: “Nobody’s perfect.” “Good things come to those who wait.” “Better late than never.”
From Wikipedia (Platitude):
- A platitude is a trite, meaningless, or prosaic statement, often used as a thought-terminating cliché, aimed at quelling social, emotional, or cognitive unease.
- Platitudes have been criticized as giving a false impression of wisdom, making it easy to accept falsehoods.
- A platitude is even worse than a cliché. It’s a sanctimonious cliché, a statement that is not only old and overused but often moralistic and imperious … Platitudes have an aphoristic quality, they seem like timeless moral lessons. They therefore shape our view of the world, and can lull us into accepting things that are actually false and foolish.
Proverb
Proverb Definition: A short, popular saying in general use stating a general truth or useful thought; usually of unknown / ancient origin that emerges from the general culture; often an epigram, maxim, or adage; often use metaphors or creative imagery.
Proverb Example: “If you chase two rabbits, you will lose them both.”
From Wikipedia (Proverb):
- A proverb is a simple, concrete, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience.
- Proverbs are often metaphorical and use formulaic language.
You May Also Enjoy:




